What are the application scenarios of PID control for frequency converters?
Introduction
Inverter PID control is a cornerstone of modern industrial automation. But what exactly is it, and where is it used? Simply put, an inverter regulates a motor’s speed, while the PID controller acts as its “intelligent brain.” This brain continuously calculates the difference between a desired setpoint and a measured feedback value from a sensor. It then dynamically adjusts the motor speed based on Proportional (P), Integral (I), and Derivative (D) actions to maintain a physical variable—like pressure or temperature—at a stable target level.
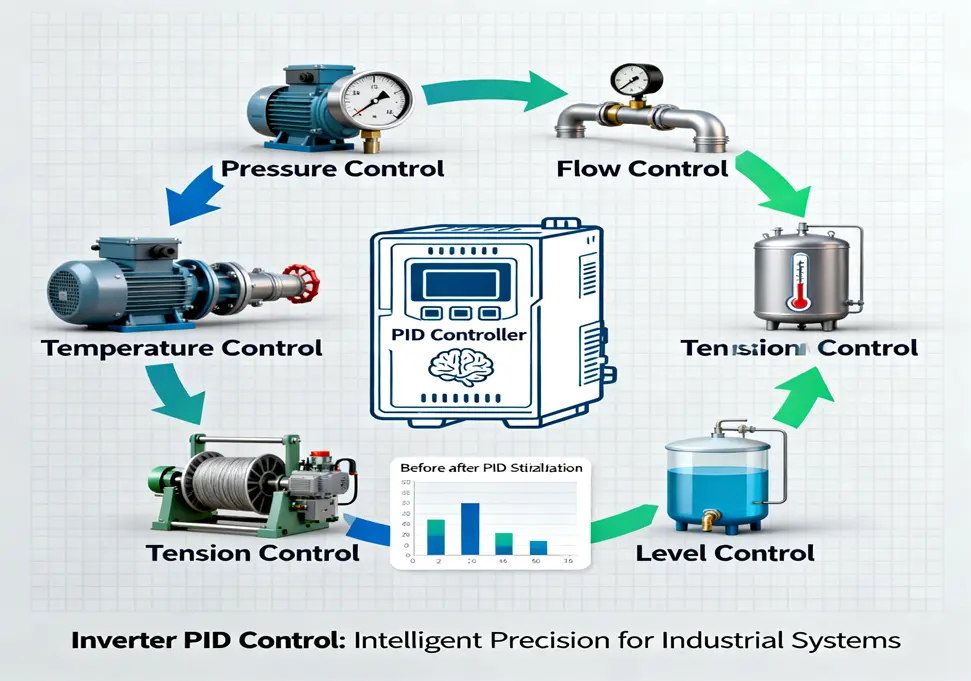
This article explores the most common and effective application scenarios for inverter PID control.
1. Pressure Control
This is one of the most classic applications, ideal for maintaining constant pressure in pipelines or vessels.
-
Constant Pressure Water Supply:
-
How It Works: A pressure transmitter installed on the water network provides real-time feedback to the inverter. The PID logic adjusts the pump motor’s speed to maintain the set pressure. When water demand increases and pressure drops, the PID increases pump speed. When demand falls, it reduces speed.
-
Key Benefits: This system replaces inefficient water towers, ensures stable water pressure, and offers significant energy savings (typically 20-40%). It also minimizes pressure shocks to the pipeline caused by frequent pump starts and stops.
-
-
Air Compressor Control:
-
How It Works: Similarly, the inverter uses feedback from a pressure sensor at the air tank’s output. The PID controller adjusts the compressor motor’s speed to deliver a stable air pressure.
-
Key Benefits: It prevents the compressor from constantly loading and unloading, reducing energy consumption and wear, thereby extending equipment life.
-
2. Flow Control
This application ensures a consistent flow rate of liquids or gasses in a process.
-
How It Works: A flow meter (e.g., electromagnetic or turbine) measures the instantaneous flow. The inverter’s PID controller uses this data to adjust the pump or fan motor speed, ensuring the flow rate precisely matches the setpoint.
-
Common Applications:
-
Chemical processing for accurate ingredient dosing.
-
Wastewater treatment for controlled chemical additive injection.
-
Food and beverage production for precise filling and mixing.
-
HVAC systems for adjusting water flow based on cooling or heating demand.
-
3. Temperature Control
PID control is highly effective for maintaining precise temperatures in environments or processes.
-
How It Works: A temperature sensor (e.g., thermocouple or RTD) provides feedback. The inverter’s PID output then controls the speed of devices like circulating fans, cooling pumps, or compressor motors to add or remove heat as needed.
-
Common Applications:
-
HVAC Systems: Adjusting chilled water pump speed based on return air temperature to optimize energy use and comfort.
-
Industrial Ovens & Heat Chambers: Regulating fan and heating element speed for uniform temperature distribution.
-
Plastic Extruders: Maintaining precise temperature zones for consistent material quality.
-
4. Tension Control
In web-handling industries, maintaining constant material tension is critical for quality and preventing breaks.
-
How It Works: A tension sensor or a dancer roller position provides the feedback signal. The PID controller automatically adjusts the speed or torque of the winder/unwinder motor to keep the material tension consistent throughout the process.
-
Common Applications:
-
Printing presses for precise color registration.
-
Paper, film, and foil converting machines.
-
Wire winding and textile fiber production.
-
5. Level Control
This application is used to maintain a specific liquid level in tanks, sumps, or reactors.
-
How It Works: A level sensor (ultrasonic, float, etc.) monitors the current liquid height. The PID controller adjusts the speed of an inlet or outlet pump to maintain the level at the desired setpoint.
-
Common Applications:
-
Automatic water replenishment in storage tanks.
-
Controlling liquid levels in wastewater treatment basins and chemical reactors.
-
Summary of Applications
| Application Scenario | Controlled Variable | Typical Feedback Sensor | Controlled Equipment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Constant Pressure Water Supply | Pressure | Pressure Transmitter | Water Pump |
| Air Compressor | Pressure | Pressure Transmitter | Air Compressor |
| Process Flow Control | Flow | Flow Meter | Pump, Fan |
| HVAC & Process Temperature | Temperature | Temperature Sensor | Pump, Fan, Compressor |
| Web Handling (Winding) | Tension | Tension Sensor, Dancer Roll | Wind/Unwind Motor |
| Tank Level Control | Level | Level Sensor | Pump |
Key Benefits of Using Inverter PID Control
-
High Precision & Stability: Maintains process variables within a tight tolerance, directly improving product quality and consistency.
-
Significant Energy Savings: By matching motor speed to the actual demand instead of using throttling valves or dampers, energy consumption is drastically reduced.
-
Full Automation: Minimizes the need for manual intervention, leading to more efficient and reliable operations.
-
Soft Start & Stop: Gently ramps motor speed up and down, reducing mechanical stress on motors, pumps, and driven equipment, which extends their service life.

