Solar panels are primarily categorized into three main types based on their materials: silicon-based, thin-film, and organic. Below is a detailed breakdown of each type:
-
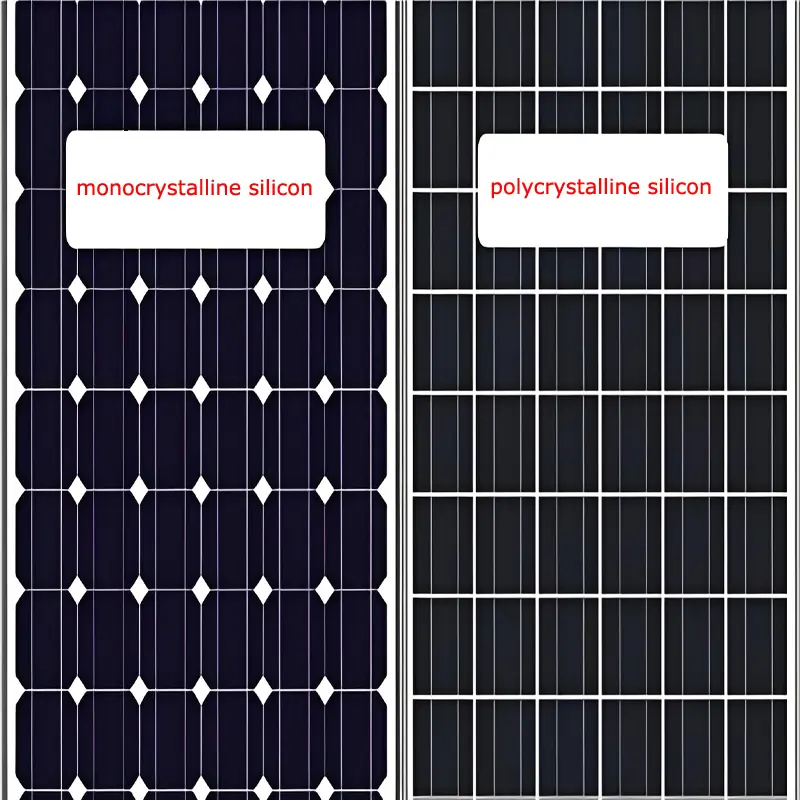
- Polycrystalline Silicon PV Panels: Fabricated from polycrystalline silicon wafers, these panels have a relatively imperfect lattice structure. They benefit from simpler manufacturing processes and lower costs, with conversion efficiency between 12% and 18% and reliable stability. Their light blue color makes them a common choice for residential installations and small-scale commercial applications.
-
Thin-film Solar Panels:
-
- Copper Indium Gallium Selenide (CIGS) PV Panels: Produced using non-silicon materials (copper, indium, gallium, and selenium), these panels are flexible and lightweight, with low material costs. Their conversion efficiency usually falls between 7% and 13%, making them suitable for flexible devices and building-integrated applications (e.g., exterior walls, rooftops).

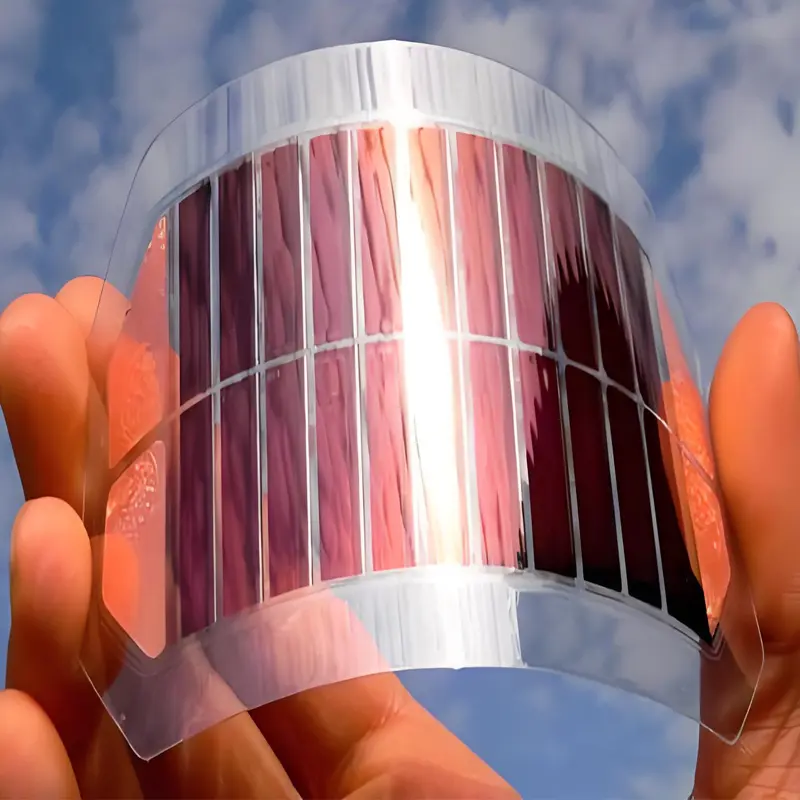
- Perovskite PV Panels: An emerging type of photovoltaic module, these panels are based on perovskite materials. Their conversion efficiency surpasses that of traditional silicon-based PV modules, with a theoretical efficiency of over 30%. Available in dark red or brown, they are easy to shape and adaptable to diverse design requirements, often used in high-end commercial and industrial settings.
- Cadmium Telluride (CdTe) PV Panels: These panels offer the same low-cost advantage as polycrystalline cells and stand out for having the lowest carbon footprint, water consumption, and energy payback time among all solar panel types. However, due to the toxicity of cadmium, their recycling costs are relatively high, and their conversion efficiency typically ranges from 8% to 12%.

- Amorphous Silicon (a-Si) PV Panels: Made from amorphous silicon, these panels feature simpler manufacturing processes and better resistance to light-induced degradation, making them suitable for low-illumination environments. That said, their conversion efficiency is relatively low (only 6% to 8%), so they are mostly used in low-power devices like pocket calculators.

-
Organic Solar Panels: Organic photovoltaic modules are manufactured using organic materials. They have straightforward production processes, low costs, and excellent flexibility and moldability—allowing them to fit various shapes. They also perform effectively under low light, making them suitable for low-power applications. However, their conversion efficiency and stability remain relatively low and require further improvement.
![]()







